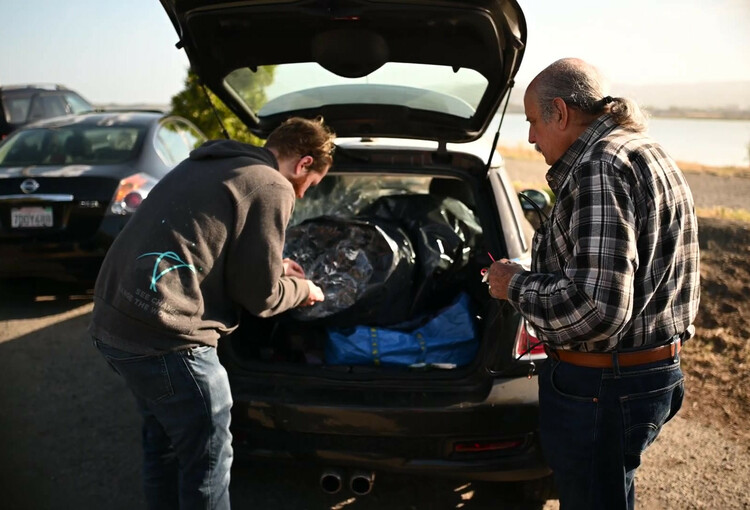
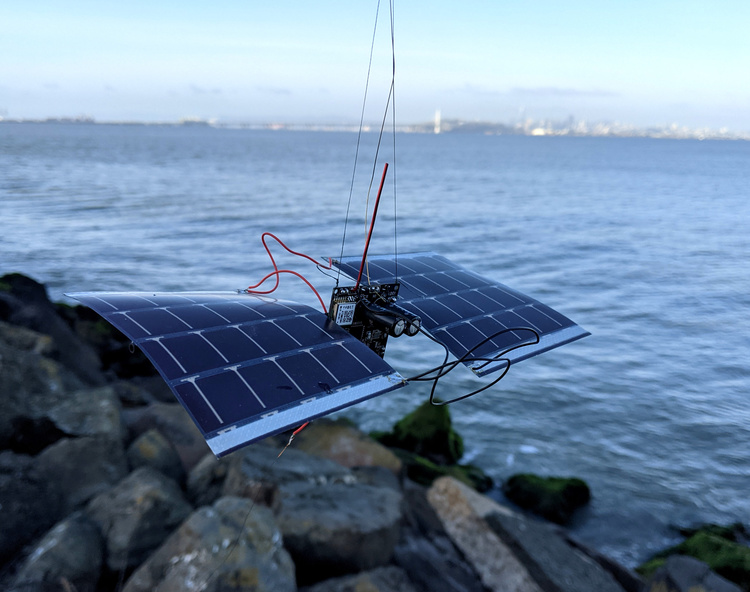
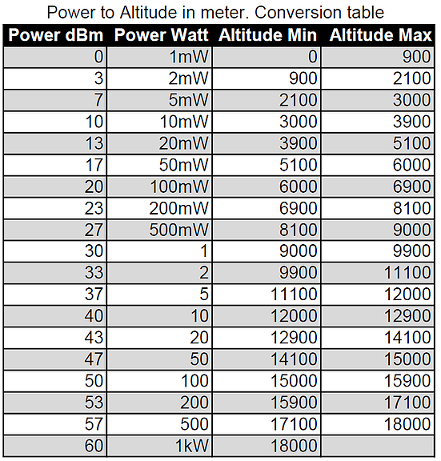
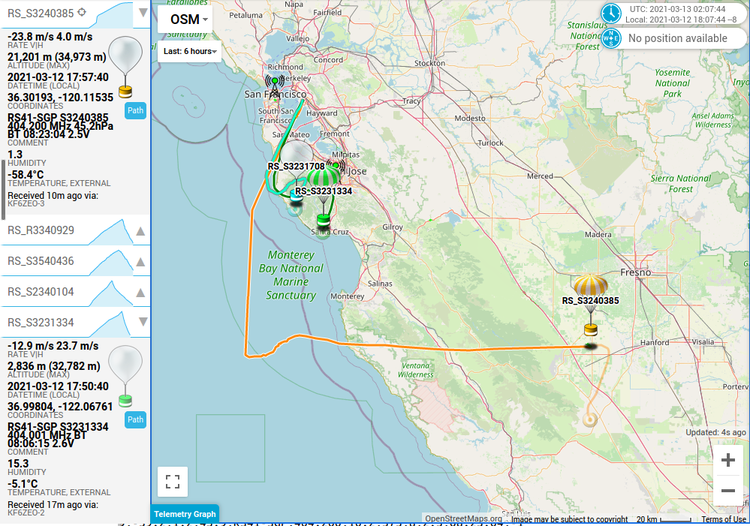
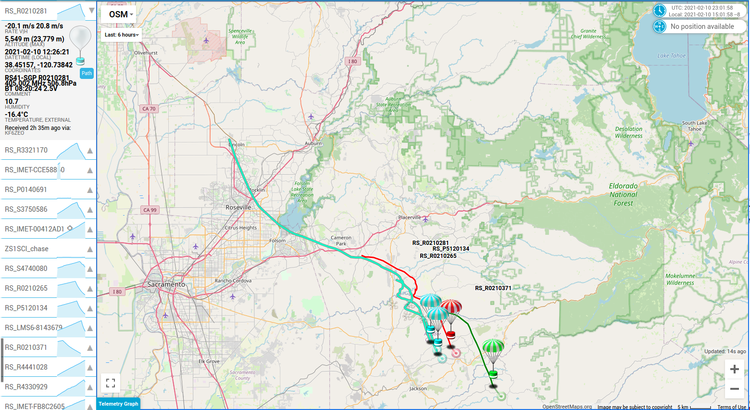
After the dissappointing results from the last balloon, we decided to respin the boards to try and fix this GPS self-interference problem. We also decided to add a low-pass filter to try and keep the WSPR transmitter harmonics out of the GPS band. The new boards did not arrive in time for the Memorial Day weekend, so we decided to launch anyways.
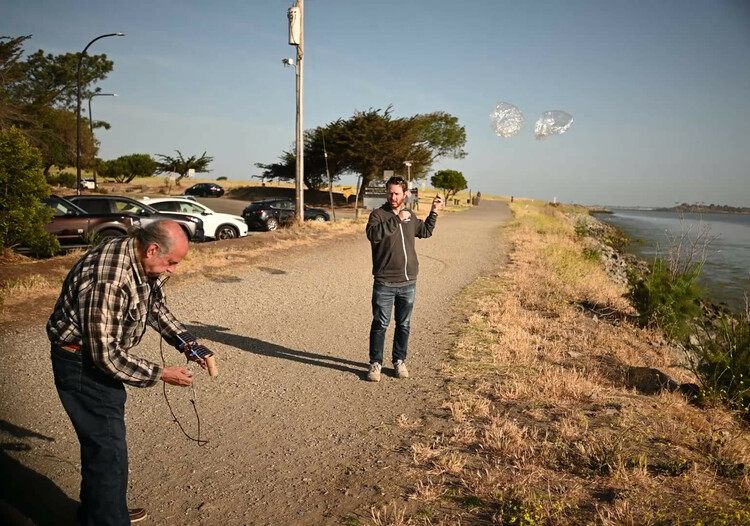
After a day delay due to strong winds and high altitude clouds, we launched on the morning of Sunday May 30th 2021. The weather was beautiful. The launch party was Martin W6MRR, Robert K6RGG, and myself KF6ZEO. We launched again from the northwest corner of the Berkeley Marina.
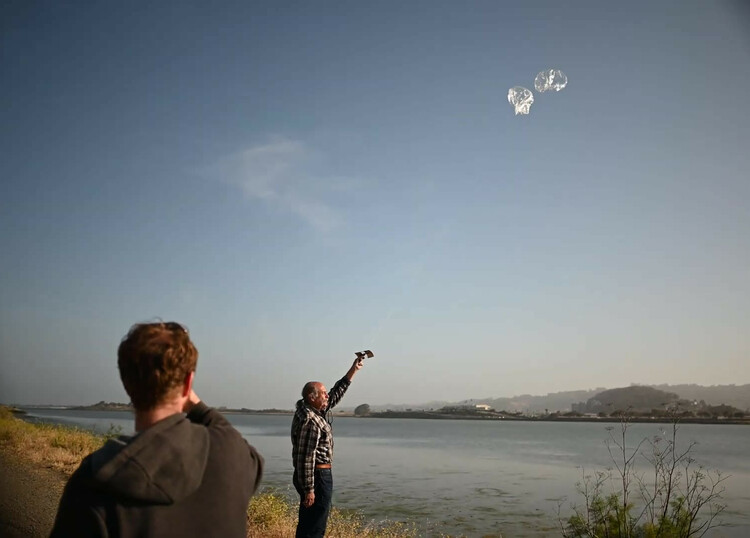
The winds were gusting to 5 knots or so, and we had to wait for a few minutes for a lull in the winds to release the picoballoon. Even a very slow wind can make the balloons bend over almost to the ground. We released the picoballoon just after 8 am local time (1500 UTC).
Robert K6RGG took a video of the preparation and launch sequence:
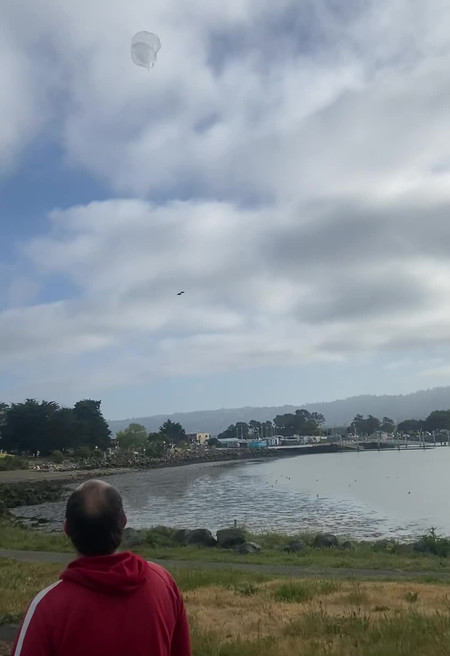
Just after launch, I ...
Read More →